Mastering Risk Management in Options Trading

Key Takeaways
- Master Position Sizing: Learn how to determine the right size for each trade to protect your portfolio.
- Diversify Effectively: Understand advanced diversification strategies to spread risk across assets, sectors, and geographies.
- Leverage Stop-Loss Orders: Utilize advanced stop-loss techniques to limit potential losses and secure profits.
- Simulate Market Scenarios: Perform scenario testing to anticipate market movements and adjust strategies accordingly.
- Implement Hedging: Use various hedging strategies to offset potential losses and safeguard your investments.
- Optimize with Tools: Discover how to use the InsiderFinance Options Profit Calculator for precise profit and loss projections.
Why It Matters
- Protect Your Investments: Minimize potential losses and safeguard your capital against adverse market movements.
- Enhance Decision-Making: Make informed trading decisions based on comprehensive risk analysis and scenario testing.
- Maximize Returns: Optimize your trading strategies to increase profitability while managing risk effectively.
- Stay Ahead of the Market: Be prepared for various market conditions, ensuring your trading success in both volatile and stable environments.
Unlock the secrets to mastering options trading with proven risk management techniques that safeguard your investments and amplify your success!
In the high-stakes world of options trading, effective risk management isn’t just an option — it’s a necessity.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through essential strategies to manage risk effectively, ensuring you make informed decisions and optimize your trading success.
Dive in to discover how to protect your portfolio, maximize returns, and navigate the complexities of options trading with confidence.
Position Sizing

Position sizing is the cornerstone of risk management in options trading. It involves determining the appropriate size of each position based on your overall portfolio and risk tolerance. Here are the key aspects:
Risk Tolerance Assessment
Understanding your risk tolerance is fundamental to position sizing:
- Questionnaires and Surveys: Many financial institutions offer risk tolerance questionnaires that help you gauge your comfort level with various levels of risk.
- Financial Health Analysis: Review your financial situation, including your income, expenses, savings, and investment goals. This analysis helps you determine how much risk you can afford to take.
- Risk Tolerance Metrics: Use metrics such as the standard deviation of returns and Value at Risk (VaR) to quantify your risk tolerance.
Portfolio Allocation Strategies
Allocating your portfolio wisely is crucial for managing risk:
Fixed Percentage Allocation: Allocate a fixed percentage of your portfolio to each trade, such as 1-2% for conservative traders or 3-5% for aggressive traders.
- A conservative trader allocates 1% of their $100,000 portfolio per trade, ensuring no single trade risks more than $1,000. This approach minimizes the impact of any single loss on the overall portfolio.
Volatility-Based Allocation: Adjust the allocation based on the volatility of the underlying asset. Higher volatility assets should have smaller position sizes.
- A trader investing in a high-volatility biotech stock allocates only 1% of their portfolio to this position, while allocating 3% to a low-volatility utility stock. This strategy balances the potential risk and reward across different assets.
Dynamic Allocation: Continuously adjust your position sizes based on market conditions and portfolio performance.
- A trader increases their position size in a tech stock during a bull market but reduces exposure during periods of high uncertainty. This dynamic approach ensures that the portfolio is always aligned with current market conditions.
Portfolio Allocation Recommendations
Conservative Approach: Allocate 1-2% of your portfolio per trade, ensuring minimal impact on your overall portfolio from any single loss.
- A trader with a $200,000 portfolio allocates $2,000 (1%) per trade, maintaining a low risk profile and safeguarding the majority of their capital.
Moderate Approach: Allocate 2-3% of your portfolio per trade, balancing risk and potential return.
- A trader with a $150,000 portfolio allocates $3,750 (2.5%) per trade, striking a balance between risk management and the potential for higher returns.
Aggressive Approach: Allocate 3-5% of your portfolio per trade, accepting higher risk for the possibility of higher returns.
- An aggressive trader with a $50,000 portfolio allocates $2,500 (5%) per trade, willing to take on more risk in pursuit of significant gains.
Diversification

Diversification is a fundamental principle in managing risk. By spreading investments across various strategies and underlying assets, you can reduce the impact of adverse movements in any single asset.
Diversification Strategies
Strategy Diversification: Employ different options strategies such as covered calls, protective puts, and iron condors. Each strategy has its risk-reward profile, and combining them can balance overall portfolio risk.
- A trader uses covered calls on tech stocks for steady income, protective puts on healthcare stocks to hedge against downturns, and iron condors on indices to benefit from stable market conditions. This mix reduces the risk of relying on a single strategy.
Asset Diversification: Invest in a variety of underlying assets, including stocks, indices, and commodities, to spread risk.
- A trader invests in tech stocks, S&P 500 index options, and gold futures. If one asset class underperforms, the others can help offset losses, providing more stable returns.
Sector Diversification: Invest in different sectors (e.g., technology, healthcare, finance) to spread risk. Market movements in one sector may not impact another, reducing overall portfolio volatility.
- A trader allocates their portfolio across technology, healthcare, and financial sectors. When tech stocks face a downturn, strong performance in healthcare and finance helps balance the overall portfolio performance.
Geographic Diversification: Allocate investments across various geographic regions to mitigate risks associated with regional economic downturns or political instability.
- A trader invests in options on U.S. tech stocks, European industrial stocks, and Asian emerging market stocks. This diversification protects against regional risks, ensuring that events in one region do not disproportionately affect the entire portfolio.
Temporal Diversification: Stagger the expiration dates of your options to avoid significant portfolio impact from market movements on a single expiration date.
- A trader has options expiring in March, June, and September. By staggering expirations, they reduce the risk of all positions being affected by a single market event, leading to more consistent returns.
HIGH POTENTIAL TRADES SENT DIRECTLY TO YOUR INBOX
Add your email to receive our free daily newsletter. No spam, unsubscribe anytime.
Stop-Loss Orders

Stop-loss orders are essential for limiting potential losses. They automatically close positions if the underlying asset price moves beyond a predetermined level, protecting your capital:
Stop-Loss Levels: Determine stop-loss levels based on technical analysis, support, and resistance levels.
- A trader sets a stop-loss just below a significant support level identified through technical analysis. This approach ensures that the stop-loss is triggered only if the asset breaks a key level, indicating a potential downtrend.
Volatility-Based Stop-Losses: Set stop-loss levels based on the asset’s volatility. For high-volatility assets, use wider stop-losses to avoid premature exits due to normal price fluctuations.
- A trader trading a high-volatility biotech stock sets a wider stop-loss at 15% below the purchase price to account for normal price swings, preventing frequent premature exits.
Time-Based Stops: Close positions after a certain period, regardless of price movement, to avoid prolonged exposure and potential market changes.
- A trader decides to close all trades after 30 days, irrespective of profit or loss, to avoid unforeseen market shifts and to reallocate capital to potentially better opportunities.
Trailing Stop-Loss: Adjust the stop-loss level as the asset price moves in your favor, locking in profits while still protecting against losses.
- A trader sets a trailing stop-loss 10% below the asset's peak price. As the stock price rises from $100 to $120, the trailing stop moves up to $108, ensuring profits are secured even if the price falls back.
Common Mistakes and Solutions
Common mistakes traders make with stop-loss orders and how to avoid them:
- Setting Stop-Losses Too Tight: Tight stop-losses can result in frequent premature exits. Solution: Use volatility-based stop-losses to accommodate normal price fluctuations.
- Ignoring Market Conditions: Market conditions can impact the effectiveness of stop-loss orders. Solution: Regularly review and adjust stop-loss levels based on current market conditions.
- Overreliance on Stop-Loss Orders: Relying solely on stop-loss orders without a comprehensive risk management strategy can be detrimental. Solution: Combine stop-loss orders with other risk management techniques, such as position sizing and diversification.
Scenario Testing

Scenario testing helps evaluate potential outcomes under various market conditions. This proactive approach enables you to make more informed decisions and prepare for different scenarios.
Simulating Market Movements
Simulating how market movements impact your positions is crucial for understanding potential risks and rewards:
Price Fluctuations: Analyze how different price movements of the underlying asset can affect your options positions. For example, test scenarios where the asset price increases or decreases by a certain percentage.
- A trader simulates a 10% increase and a 10% decrease in the price of a tech stock they hold call options on, assessing the potential profit or loss in each scenario to better plan their exit strategy.
Volatility Changes: Evaluate the impact of changes in market volatility on your options. Higher volatility can increase option prices, while lower volatility can decrease them.
- A trader holding options on a biotech stock runs scenarios with varying volatility levels, understanding that a rise in volatility could significantly boost the option's value, while a drop could reduce it.
Interest Rate Variations: Consider how changes in interest rates might influence your options, particularly if you hold options with longer maturities.
- A trader with long-term options on a financial sector ETF simulates different interest rate changes to see how rising rates might lower the option's value, while falling rates might enhance it.
Contingency Planning
Developing contingency plans for different scenarios ensures you are prepared for various market conditions:
Predefined Action Plans: Create predefined action plans for scenarios such as significant market drops, unexpected volatility spikes, or economic events. These plans should outline specific steps to take, such as adjusting positions or implementing hedges.
- A trader prepares for a potential market crash by planning to quickly buy protective puts on major holdings if the market drops by more than 10% in a single day, ensuring they can act swiftly to protect their portfolio.
Risk Mitigation Strategies: Identify and implement risk mitigation strategies, such as diversifying positions, adjusting stop-loss levels, or using protective options strategies.
- A trader mitigates risk by setting tighter stop-loss levels during times of high market volatility and diversifying their options strategies across different sectors to spread risk.
Risk Assessment
Assessing the risk associated with each scenario helps you understand potential losses and devise strategies to mitigate them:
- Quantitative Analysis: Use quantitative analysis to measure the potential impact of different scenarios on your portfolio. Tools like Value at Risk (VaR) and stress testing can provide insights into worst-case scenarios.
- Qualitative Assessment: Consider qualitative factors such as market sentiment, geopolitical events, and economic indicators that could influence market conditions.
Hedging

Hedging strategies are crucial for offsetting potential losses in your primary positions. By using complementary strategies, you can protect against adverse market movements:
Protective Puts: Purchase protective puts to hedge against downside risk in a long position.
- A trader with a significant long position in a tech stock uses a protective put to hedge against a potential earnings miss. When the stock drops by 15% after disappointing earnings, the put option gains value, offsetting the loss.
Covered Calls: Write covered calls to generate income and provide a cushion against minor price declines in a stock you own.
- A trader owns shares of a stable utility company and writes covered calls to generate additional income. If the stock price remains flat or slightly decreases, the income from the call options helps offset minor losses.
Options Spreads: Utilize spreads such as bull spreads, bear spreads, and butterfly spreads to limit potential losses while still maintaining some upside potential. These strategies involve buying and selling multiple options contracts to create a net position that mitigates risk.
- A trader with a long position in a high-volatility biotech stock uses a bear put spread (buying a put and selling another put at a lower strike price) to hedge against potential declines. This strategy limits the cost of the hedge while providing downside protection.
Synthetic Positions: Create synthetic positions using options to mimic the payoff of holding the underlying asset. For example, a synthetic long position involves buying a call option and selling a put option at the same strike price.
- A trader creates a synthetic long position in a blue-chip stock by buying a call option and selling a put option at the same strike price. This setup mimics holding the stock directly but with potentially lower initial capital outlay.
Delta Hedging: Use delta hedging to neutralize the directional risk of an options position. By adjusting the quantity of the underlying asset held, you can offset changes in the option's value due to price movements of the underlying asset.
- A trader with a portfolio of call options continuously adjusts their holdings in the underlying stock to maintain a delta-neutral position. This strategy helps manage risk by reducing the portfolio's sensitivity to price movements in the underlying asset.
Combining Hedging with Other Risk Management Techniques
Effective hedging involves integrating hedging strategies with other risk management techniques:
Diversification and Hedging: Combine diversification with hedging to spread risk across different assets and strategies. This approach reduces the likelihood of significant losses from any single event.
- A trader diversifies their portfolio by investing in various sectors such as technology, healthcare, and energy, and uses protective puts on the most volatile stocks. This combination helps manage sector-specific risks and provides a safety net against large downturns in any single stock.
Position Sizing and Hedging: Use appropriate position sizing to limit exposure and enhance the effectiveness of hedging strategies. Smaller position sizes can reduce the cost and complexity of hedging.
- A trader allocates only 2% of their portfolio to each trade and uses delta hedging to adjust their positions dynamically. This strategy minimizes the impact of any single trade on the overall portfolio and ensures that the cost of hedging remains manageable.
Scenario Testing and Hedging: Regularly perform scenario testing to evaluate the effectiveness of your hedging strategies under different market conditions. Adjust your hedging approach based on the results of these tests.
- A trader conducts scenario testing to simulate a market crash, rising interest rates, and increased volatility. Based on the results, they adjust their hedging strategies by increasing the use of options spreads and adding more diversified hedges to their portfolio, ensuring robust protection against varied market conditions.
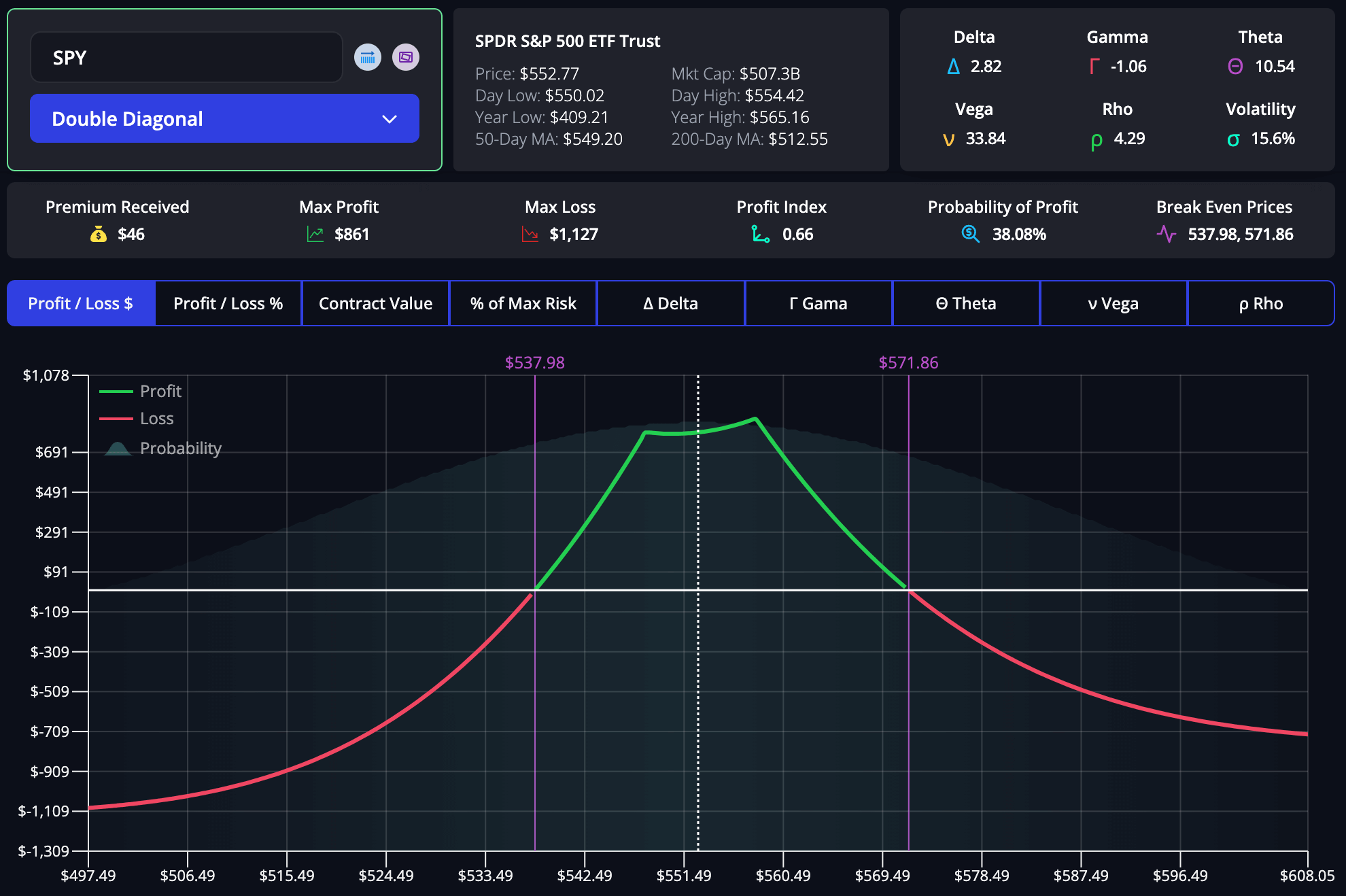
Using an Options Profit Calculator
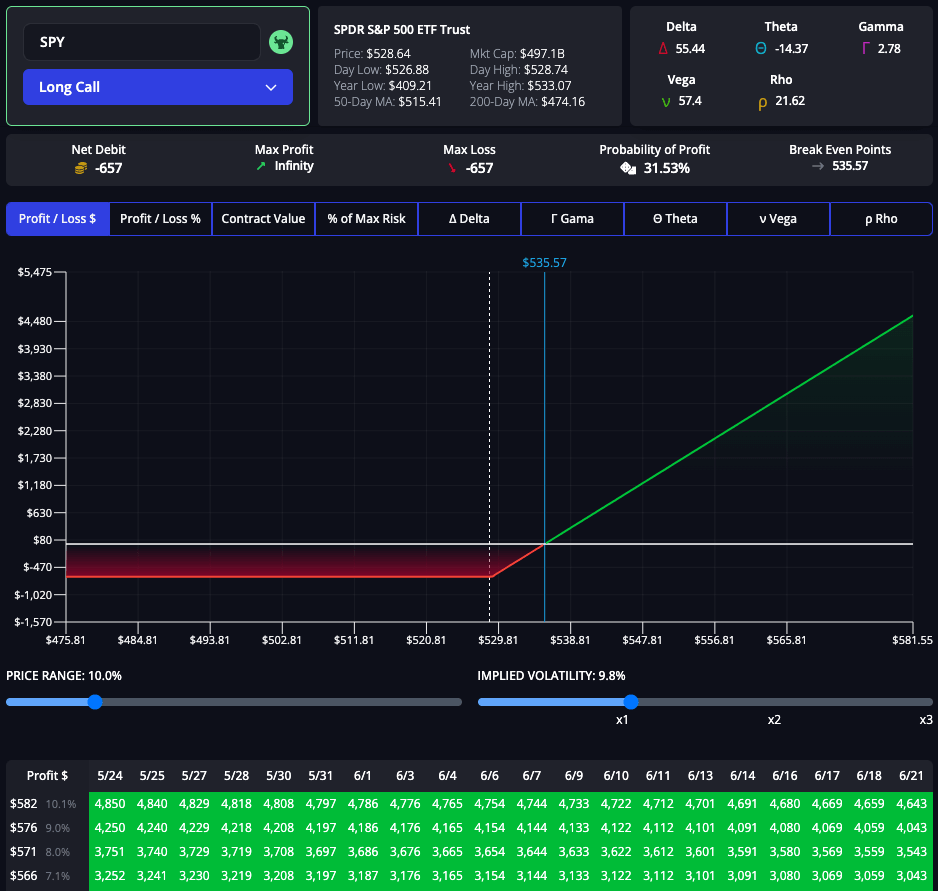
An options profit calculator is essential in managing risk and optimizing your trading strategies. The InsiderFinance Options Profit Calculator stands out for its accuracy and user experience.
Feature Breakdown
The InsiderFinance Options Profit Calculator offers several advanced features:
- Profit and Loss Projections: Provides detailed profit and loss projections for various market scenarios, helping you make informed decisions.
- Greeks Analysis: Analyzes the Greeks (Delta, Gamma, Theta, Vega, and Rho) to help you understand how different factors impact your options positions.
- Volatility Analysis: Evaluates the impact of changes in market volatility on your options trades, providing insights into how volatility can affect potential profits and losses.
- Time Decay Analysis: Assesses the impact of time decay on your options positions, helping you understand how the passage of time affects the value of your options.
Benefits of Using the InsiderFinance Options Profit Calculator
- Informed Decision-Making: Provides detailed insights into potential outcomes, helping you make informed trading decisions.
- Risk Management: Helps you assess and manage risk by simulating various market scenarios and evaluating potential losses.
- Strategy Optimization: Allows you to optimize your trading strategies based on detailed analysis, improving your chances of success.
- Enhanced Confidence: Increases your confidence in your trading decisions by providing accurate and comprehensive analysis.
Bull Call Spread Example
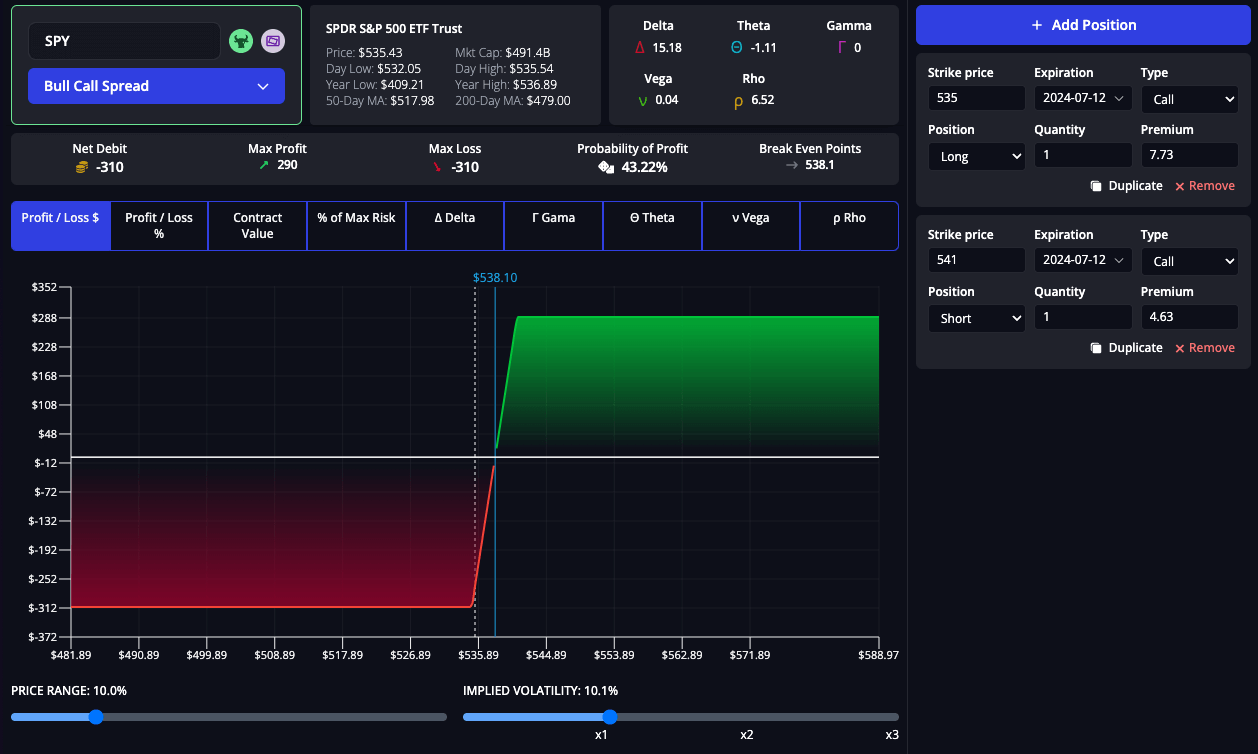
A trader uses the InsiderFinance Options Profit Calculator to analyze a bull call spread.
Option Legs:
- $535 Long Call with 30-day Expiration
- $541 Short Call with 30-day Expiration
Options Profit Calculator Analysis with 1x Volatility:
- Premium Paid: $310
- Max Profit: $290
- Max Loss: -$310
- Probability of Profit: 43.22%
- Breakeven Price: $538.10
Options Profit Calculator Analysis with 2x Volatility:
- Probability of Profit: Increases to 46.57%
Options Profit Calculator Analysis with 3x Volatility:
- Probability of Profit: Increases to 47.73%
By leveraging the features and benefits of the InsiderFinance Options Profit Calculator, the trader can see how changes in the underlying asset price and volatility impact potential profits and losses. This analysis helps the trader decide whether to proceed with the trade or adjust the strategy.
Elevate Your Options Trading with Risk Management
Mastering risk management is essential for success in options trading. By employing techniques such as position sizing, diversification, stop-loss orders, scenario testing, and hedging, traders can protect their portfolios and optimize their strategies.
Additionally, utilizing tools like the InsiderFinance Options Profit Calculator provides valuable insights and projections, ensuring you are well-prepared for various market conditions. Implement these strategies to enhance your trading success and achieve your financial goals.
HIGH POTENTIAL TRADES SENT DIRECTLY TO YOUR INBOX
Add your email to receive our free daily newsletter. No spam, unsubscribe anytime.
FAQs
What is position sizing in options trading?
Position sizing determines the amount of capital allocated to each trade based on your risk tolerance and portfolio size, helping manage potential losses.
How do I assess my risk tolerance for options trading?
Assess your risk tolerance through questionnaires, financial health analysis, and risk metrics like standard deviation and Value at Risk (VaR).
What are the best diversification strategies for options trading?
Diversify by using various strategies (e.g., covered calls, protective puts), investing in different sectors, and spreading investments across geographic regions.
How do stop-loss orders help in managing risk?
Stop-loss orders automatically close positions if the asset price moves beyond a set level, limiting potential losses and protecting your capital.
What are advanced stop-loss techniques?
Advanced techniques include volatility-based stop-losses, time-based stops, and trailing stop-losses to provide flexible and effective risk management.
How does scenario testing improve options trading strategies?
Scenario testing evaluates potential outcomes under different market conditions, helping traders prepare and adjust strategies for various scenarios.
What is hedging, and how does it work in options trading?
Hedging involves using strategies like options spreads, synthetic positions, and delta hedging to offset potential losses in primary positions.
Why is the InsiderFinance Options Profit Calculator essential for traders?
The InsiderFinance Options Profit Calculator provides accurate profit and loss projections, detailed analysis, and user-friendly features to optimize trading strategies.
How can I use the InsiderFinance Options Profit Calculator effectively?
Input trade details, analyze scenarios, evaluate profit and loss projections, and adjust strategies based on comprehensive insights provided by the calculator.
What common mistakes should I avoid in options trading risk management?
Avoid setting stop-losses too tight, ignoring market conditions, and overrelying on stop-loss orders without integrating other risk management techniques like diversification and hedging.